Inputs for a Glint and Glare Study
Solar Glint and Glare Assessment
Every Solar Glare Assessment is based on a glare calculation, utilizing specialized software to calculate the path of reflected sunlight for the glaring hazard (e.g. the solar pv plant).
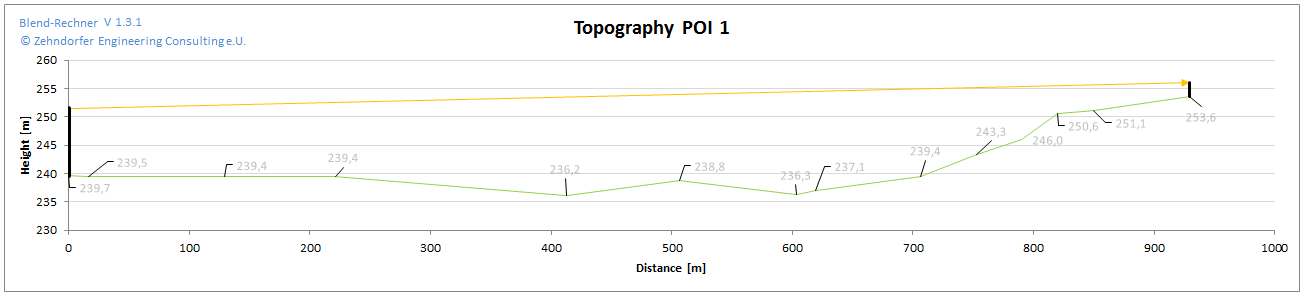
It will first and foremost clarify, if and how long sunlight will be reflected in the direction of specific points of interest. This requires the exact registration of the local environment (x/y/z-coordinates and angles) of the reflecting surfaces as well as the point of interest. A topographical profile shows if direct rays of sunlight would at all be possible, or if they would be hampered by obstacles such as raised terrain, houses or trees.
Solar Glint and Glare Calculation
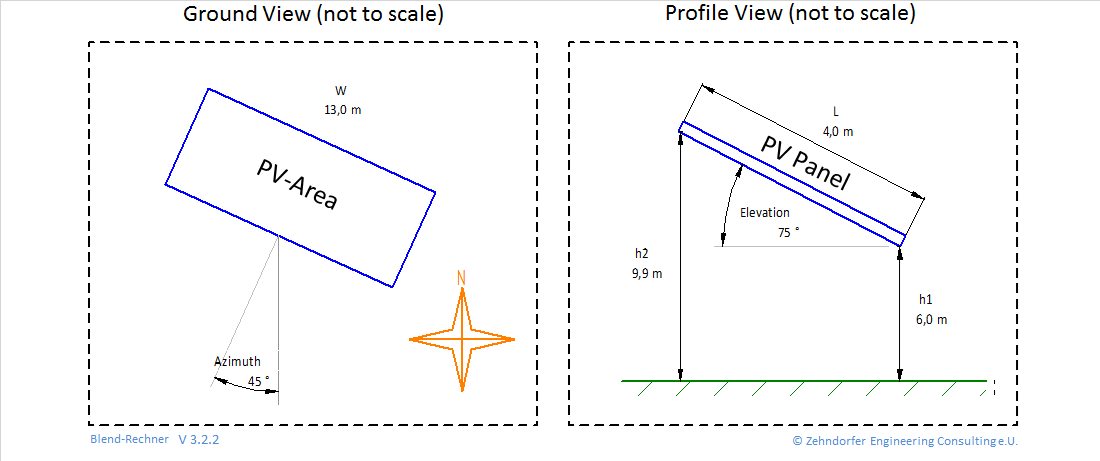 A detailed glint and glare calculation allows the optimization of reflecting areas. Small changes in the azimuth and slope angles of PV-areas can reduce or completely avoid glaring on certain points for instance. A glare calculation is the only means to quantify the glare hazard potential and thus provide a basis for a respective risk assessment.
A detailed glint and glare calculation allows the optimization of reflecting areas. Small changes in the azimuth and slope angles of PV-areas can reduce or completely avoid glaring on certain points for instance. A glare calculation is the only means to quantify the glare hazard potential and thus provide a basis for a respective risk assessment.
Contents of a Solar Glare Study
Glare-Time Diagram
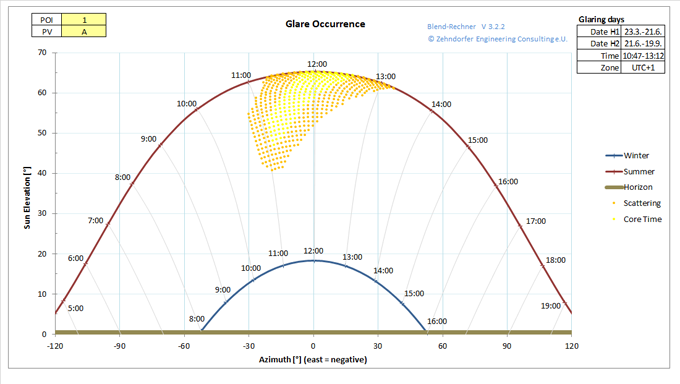
The glare-time diagram displays the distribution of potential glaring over the time of he year and the daytime. It shows if, when and how long reflection will be present. Thereby the duration of glaring in days per year and hours per day can be read from the diagram. The diagram also allows the simple illustration of the glare reducing impact of far-shading (e.g. mountains) or local shading measurements.
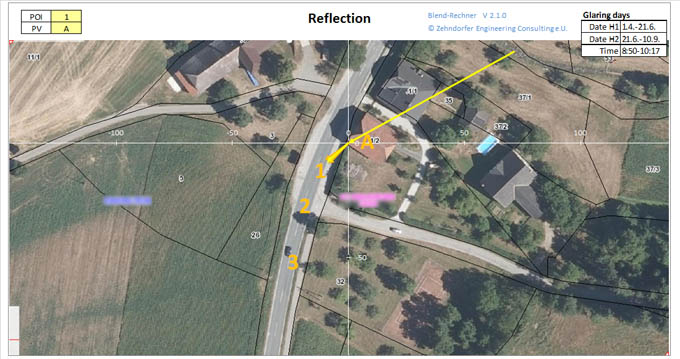
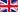
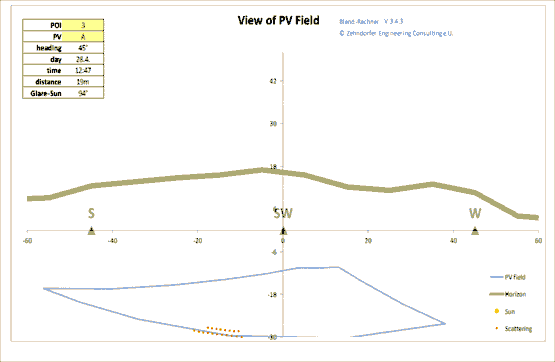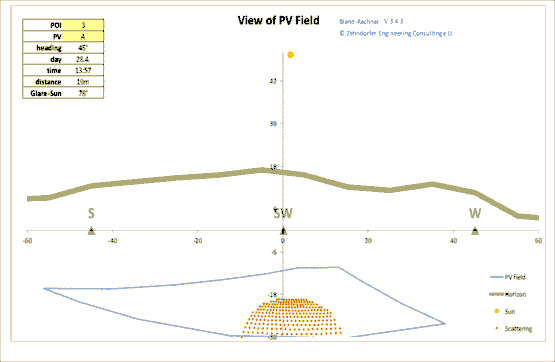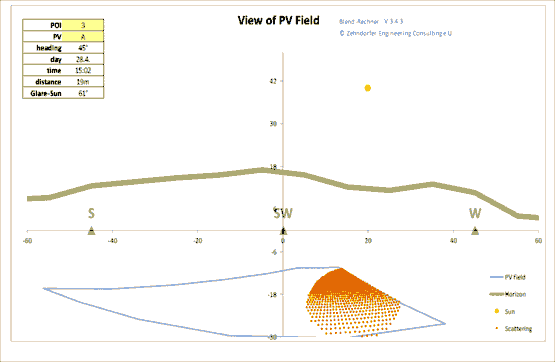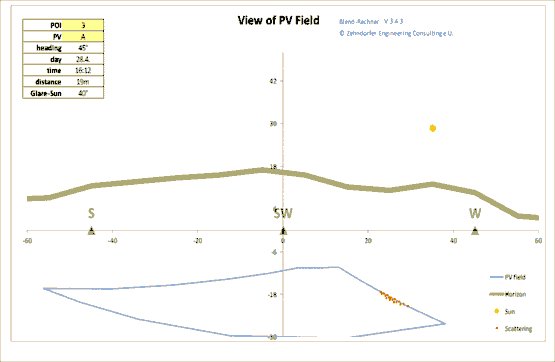
Sunlight Reflection Trail
The reflection trail sun - reflector - Point of interest shows the angle of a potential solar reflection. In some situations it becomes evident, that the necessary shown sun-position can never be reached (when the sun is too far north or when the point of interest lies behind the solar panel for example).
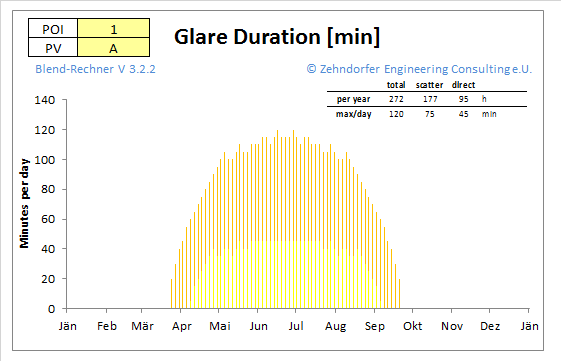
Duration of a Glaring Hazard
Being a core result of any glare calculation, the duration of glaring (by direct reflection or scattered light) can be read from the glaring-time diagram. Only a professional glare-software can calculate the glare duration accurately.
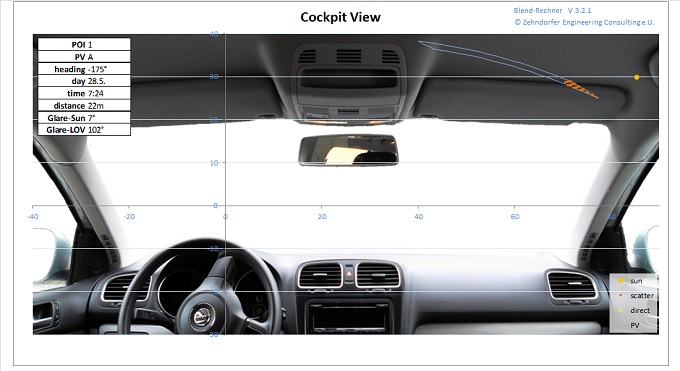
Glaring in the cockpit
The cockpit-view shows the virtual view of the reflecting area from the car. Also sun-position and reflections are displayed in this illustration. This representation of the numbers obtained by the glaring calculation provides for a more intuitive understanding of the facts by the client, the surveyor and the verifying authority.
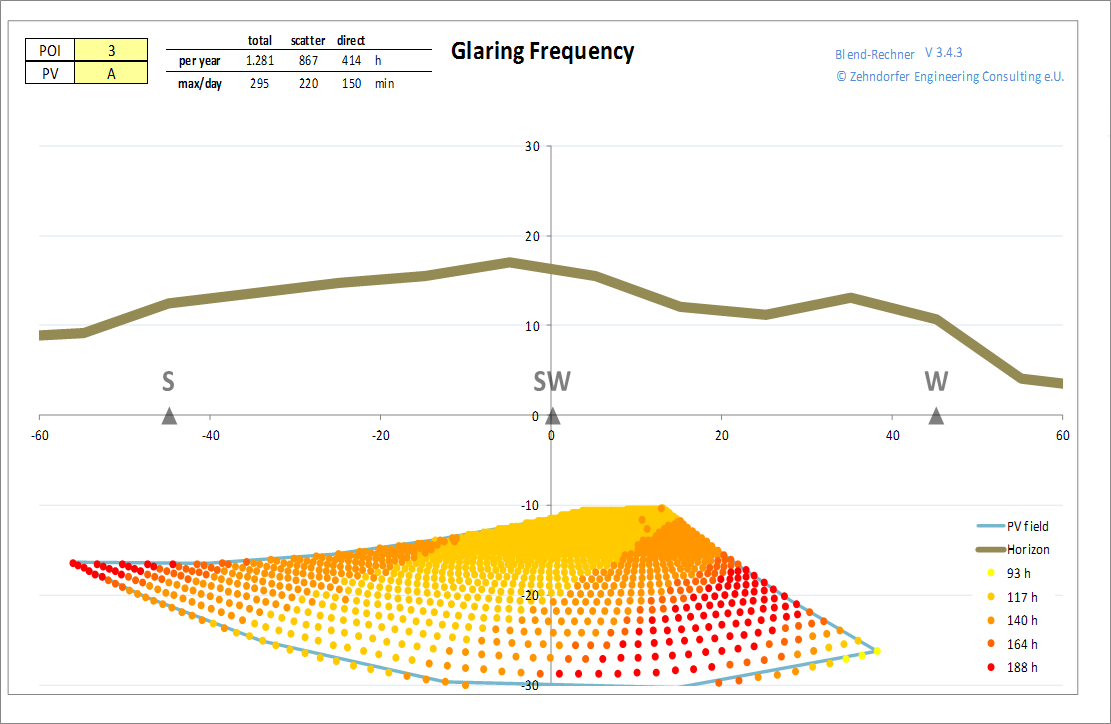
Frequency of Glint and Glare
The glaring frequency plot shows the distribution of reflection points across the reflecting surface. This allows an assessment of the complete surface and such is the basis for optimized and effective counter measures. Shading, obscuring or otherwise changing the surface can now be focused on where it counts most.
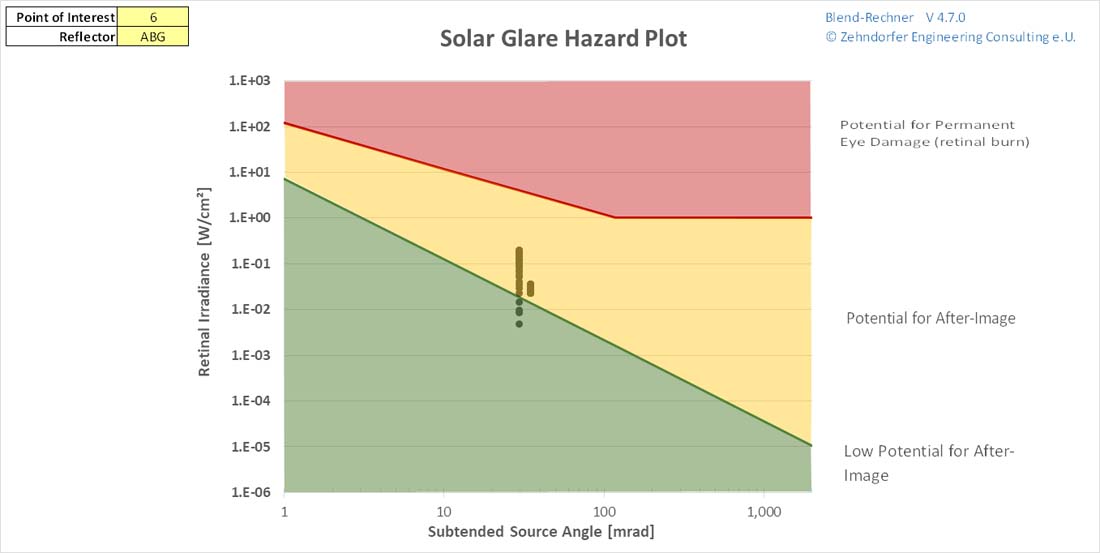
Solar Glare Hazard Plot
The Ocular Glare Hazard Plot has been developed to show the potential impact of a glaring hazard on the human eye. It is calculated with the time dependent intensity of the sun and the reflection coefficient of the reflecting surface. A glaring hazard is rated depending on two logarithmic scales - the power and the visible size of the reflections. These values are compared to limits that had been determined in experiments to cause temporary after-images or the permanent damage of the eye.
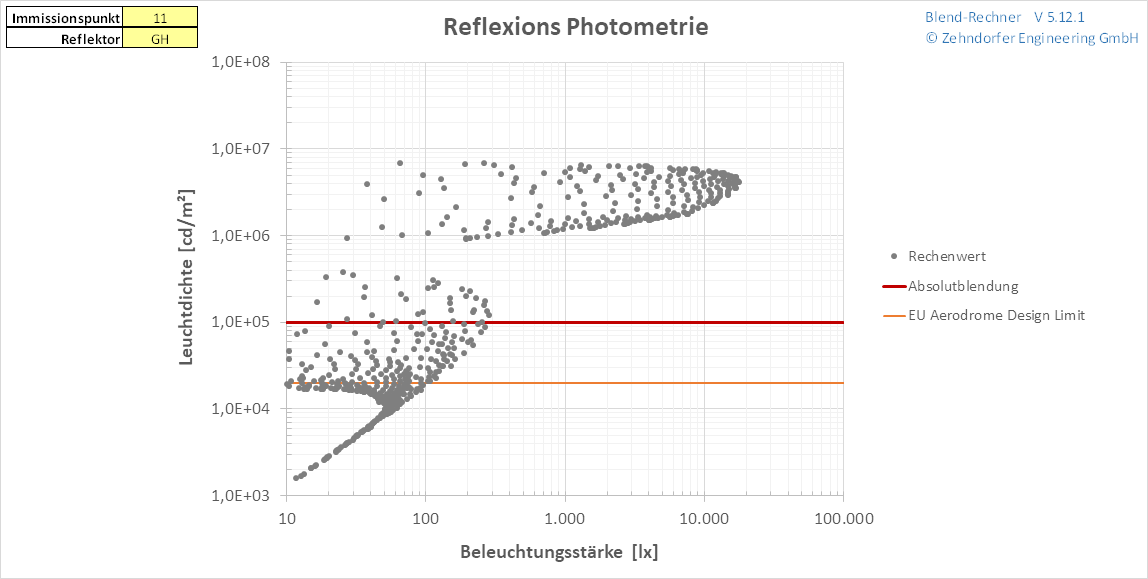
Photometric Data Calculation
While normally only the geometric conditions of reflections are calculated, photometric data can have an impact on glare perception, too. Luminance as well as Illumination play a decisive role in the standardisation and evaluation of luminaires. On one hand sufficient illumination is required, on the other hand luminaires must not dazzle humans directly. Guidelines for sun reflections also set luminance limits for just and reasonable glare dazzle. The advantage of this more detailed simulation method lies in the possibility to simulate the effect of glare-reduced glasses. Typically, only specular reflection calculations are executed (i.e. exit angle = angle of incidence). Photometric Data Calculation, however, also allows the consideration of times of weak reflections. Now these periods can be subtracted from the total glare duration, even if specular reflections exist, thus resulting in a more realistic representation.
Jakob Zehndorfer is Expert Witness for Glare Assessments at the Austrian Court of Law.